变量
变量表示命名的内存空间,将数据放在内存空间中,通过变量名引用,获取数据
变量类型
变量类型:
- 内置变量,如:PS1,PATH,UID,HOSTNAME,$$,BASHPID,PPID,$?,HISTSIZE
- 用户自定义变量
不同的变量存放的数据不同,决定了以下
-
数据存储方式
-
参与的运算
-
表示的数据范围
变量数据类型:
- 字符
- 数值:整型、浮点型,bash 不支持浮点数
编程语言分类
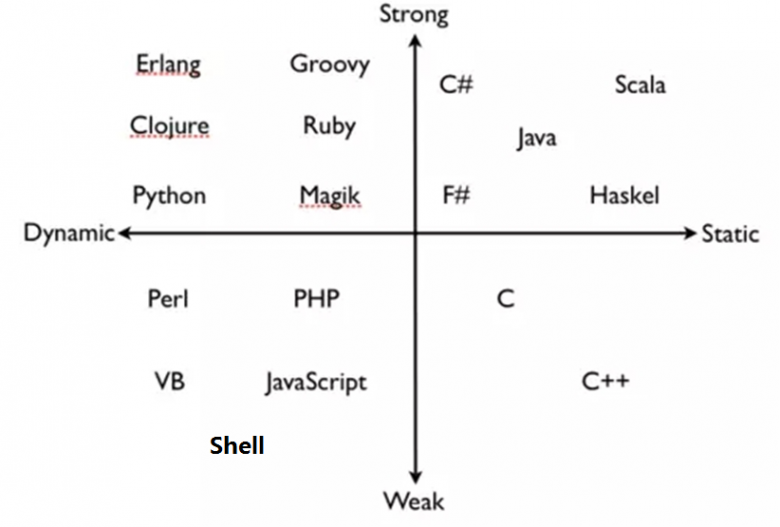
静态和动态语言
- 静态编译语言:使用变量前,先声明变量类型,之后类型不能改变,在编译时检查,如:java,c
- 动态编译语言:不用事先声明,可随时改变类型,如:bash,Python
强类型和弱类型语言
- 强类型语言:不同类型数据操作,必须经过强制转换才同一类型才能运算,如java , c# ,python 如:以下python代码 print(‘magedu’+ 10) 提示出错,不会自动转换类型 print(‘magedu’+str(10)) 结果为magedu10,需要显示转换类型
- 弱类型语言:语言的运行时会隐式做数据类型转换。无须指定类型,默认均为字符型;参与运算会自动进行隐式类型转换;变量无须事先定义可直接调用 如:bash ,php,javascript
Shell中变量命名法则
- 不能使程序中的保留字:如:if, for
- 只能使用数字、字母及下划线,且不能以数字开头,注意:不支持短横线 “ – ”,和主机名相反
- 见名知义,用英文单词命名,并体现出实际作用,不要用简写,如:ATM
- 统一命名规则:驼峰命名法, studentname,大驼峰StudentName 小驼峰studentName
- 变量名大写:STUDENT_NAME
- 局部变量小写
- 函数名小写
变量定义和引用
变量的生效范围等标准划分变量类型
- 普通变量:生效范围为当前shell进程;对当前shell之外的其它shell进程,包括当前shell的子shell进程均无效
- 环境变量:生效范围为当前shell进程及其子进程
- 本地变量:生效范围为当前shell进程中某代码片断,通常指函数
变量赋值:
name='value'
value 可以是以下多种形式
直接字串:name='root'
变量引用:name="$USER"
命令引用:name=COMMAND 或者 name=$(COMMAND)
注意:变量赋值是临时生效,当退出终端后,变量会自动删除,无法持久保存,脚本中的变量会随着脚本结束,也会自动删除
变量引用:
$name ${name}
弱引用和强引用
- “$name ” 弱引用,其中的变量引用会被替换为变量值
- ‘$name ‘ 强引用,其中的变量引用不会被替换为变量值,而保持原字符串
范例:变量的各种赋值方式
[root@centos8 ~]#TITLE='cto'
[root@centos8 ~]#echo $TITLE
cto
[root@centos8 ~]#echo I am $TITLE
I am cto
[root@centos8 ~]#echo "I am $TITLE"
I am cto
[root@centos8 ~]#echo 'I am $TITLE'
I am $TITLE
[root@centos8 ~]#NAME=$USER
[root@centos8 ~]#echo $NAME
root
[root@centos8 ~]#USER=whoami
[root@centos8 ~]#echo $USER
root
[root@centos8 ~]#FILE=ls /run
[root@centos8 ~]#echo $FILE
agetty.reload atd.pid auditd.pid autofs.fifo-misc autofs.fifo-net console cron.reboot cryptsetup dbus faillock fsck initctl initramfs lock log mount NetworkManager plymouth rsyslogd.pid screen sepermit setrans sshd.pid sssd.pid sudo systemd tmpfiles.d tuned udev user utmp vmware
[root@centos8 ~]#FILE=/etc/*
[root@centos8 ~]#echo $FILE
/etc/adjtime /etc/aliases /etc/alternatives /etc/anacrontab /etc/at.deny /etc/audit /etc/authselect /etc/autofs.conf /etc/autofs_ldap_auth.conf
[root@centos8 ~]#seq 10
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
[root@centos8 ~]#NUM=seq 10
[root@centos8 ~]#echo $NUM
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10
[root@centos8 ~]#echo "$NUM"
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
[root@centos8 ~]#NAMES="wang
> zhang
> zhao
> li"
[root@centos8 ~]#echo $NAMES
wang zhang zhao li
[root@centos8 ~]#echo "$NAMES"
wang
zhang
zhao
li
范例:变量的间接赋值和引用
[root@centos8 ~]#TITLE=cto
[root@centos8 ~]#NAME=wang
[root@centos8 ~]#TITLE=$NAME
[root@centos8 ~]#echo $NAME
wang
[root@centos8 ~]#echo $TITLE
wang
[root@centos8 ~]#NAME=mage
[root@centos8 ~]#echo $NAME
mage
[root@centos8 ~]#echo $TITLE
wang
范例:
[root@centos8 data]#NAME=mage
[root@centos8 data]#AGE=20
[root@centos8 data]#echo $NAME
mage
[root@centos8 data]#echo $AGE
20
[root@centos8 data]#echo $NAME $AGE
mage 20
[root@centos8 data]#echo $NAME$AGE
mage20
[root@centos8 data]#echo $NAME_$AGE
20
[root@centos8 data]#echo ${NAME}_$AGE
mage_20
范例:利用变量实现动态命令
[root@centos8 ~]#CMD=hostname
[root@centos8 ~]#$CMD
centos8.wangxiaochun.com
显示已定义的所有变量:
set
删除变量:
unset <name>
范例:
[root@centos8 ~]#NAME=mage [root@centos8 ~]#TITLE=ceo [root@centos8 ~]#echo $NAME $TITLE mage ceo [root@centos8 ~]#unset NAME TITLE [root@centos8 ~]#echo $NAME $TITLE
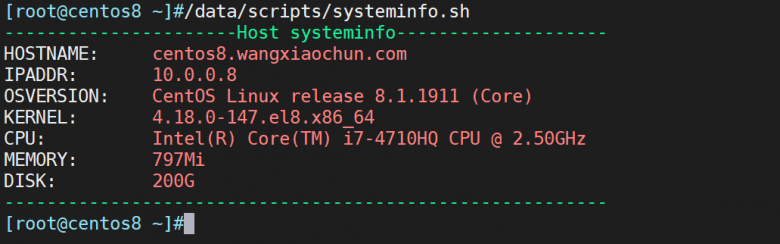
范例:显示系统信息
[root@centos8 scripts]#cat systeminfo.sh
#
#********************************************************************
#Author: wangxiaochun
#QQ: 29308620
#Date: 2019-12-23
#FileName: systeminfo.sh
#URL: http://www.magedu.com
#Description: Show system information
#Copyright (C): 2019 All rights reserved
#********************************************************************
RED="\E[1;31m"
GREEN="\E[1;32m"
END="\E[0m"
echo -e "$GREEN----------------------Host systeminfo--------------------$END"
echo -e "HOSTNAME: $REDhostname$END"
echo -e "IPADDR: $RED ifconfig eth0|grep -Eo '([0-9]{1,3}\.){3}[0-9]{1,3}' |head -n1$END"
echo -e "OSVERSION: $REDcat /etc/redhat-release$END"
echo -e "KERNEL: $REDuname -r$END"
echo -e "CPU: $REDlscpu|grep 'Model name'|tr -s ' '|cut -d : -f2$END"
echo -e "MEMORY: $REDfree -h|grep Mem|tr -s ' ' : |cut -d : -f2$END"
echo -e "DISK: $REDlsblk |grep '^sd' |tr -s ' ' |cut -d "</span> <span class="cm-string">" -f4$END"
echo -e "$GREEN---------------------------------------------------------$END"
[root@centos8 scripts]#cat systeminfo.sh
#
#********************************************************************
#Author: wangxiaochun
#QQ: 29308620
#Date: 2019-12-23
#FileName: systeminfo.sh
#URL: http://www.magedu.com
#Description: Show system information
#Copyright (C): 2019 All rights reserved
#********************************************************************
RED="\E[1;31m"
GREEN="echo -e \E[1;32m"
END="\E[0m"
$GREEN----------------------Host systeminfo--------------------$END
echo -e "HOSTNAME: $REDhostname$END"
echo -e "IPADDR: $RED ifconfig eth0|grep -Eo '([0-9]{1,3}\.){3}[0-9]{1,3}' |head -n1$END"
echo -e "OSVERSION: $REDcat /etc/redhat-release$END"
echo -e "KERNEL: $REDuname -r$END"
echo -e "CPU: $REDlscpu|grep 'Model name'|tr -s ' '|cut -d : -f2$END"
echo -e "MEMORY: $REDfree -h|grep Mem|tr -s ' ' : |cut -d : -f2$END"
echo -e "DISK: $REDlsblk |grep '^sd' |tr -s ' ' |cut -d "</span> <span class="cm-string">" -f4$END"
$GREEN---------------------------------------------------------$END
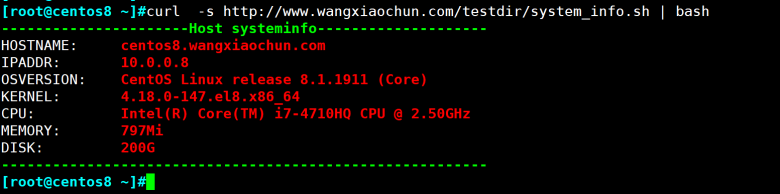
练习:
1、编写脚本 systeminfo.sh,显示当前主机系统信息,包括:主机名,IPv4地址,操作系统版本,内核版本,CPU型号,内存大小,硬盘大小 2、编写脚本 backup.sh,可实现每日将/etc/目录备份到/backup/etcYYYY-mm-dd中 3、编写脚本 disk.sh,显示当前硬盘分区中空间利用率最大的值 4、编写脚本 links.sh,显示正连接本主机的每个远程主机的IPv4地址和连接数,并按连接数从大到小排序
环境变量
环境变量:
- 可以使子进程(包括孙子进程)继承父进程的变量,但是无法让父进程使用子进程的变量
- 一旦子进程修改从父进程继承的变量,将会新的值传递给孙子进程
- 一般只在系统配置文件中使用,在脚本中较少使用
变量声明和赋值:
#声明并赋值 export name=VALUE declare -x name=VALUE #或者分两步实现 name=VALUE export name
变量引用:
$name
${name}
显示所有环境变量:
env printenv export declare -x
删除变量:
unset name
bash内建的环境变量
PATH
SHELL
USER
UID
HOME
PWD
SHLVL #shell的嵌套层数,即深度
LANG
MAIL
HOSTNAME
HISTSIZE
_ #下划线 表示前一命令的最后一个参数
只读变量
只读变量:只能声明定义,但后续不能修改和删除,即常量
声明只读变量:
readonly name
declare -r name
查看只读变量:
readonly [-p]
declare -r
范例:
[root@centos8 ~]#readonly PI=3.14159 [root@centos8 ~]#echo $PI 3.14159 [root@centos8 ~]#PI=3.14 -bash: PI: readonly variable [root@centos8 ~]#unset PI -bash: unset: PI: cannot unset: readonly variable [root@centos8 ~]#echo $PI 3.14159 [root@centos8 ~]#exit logout Connection closed by foreign host. Disconnected from remote host(10.0.0.8) at 14:27:04. Type `help' to learn how to use Xshell prompt. [c:\~]$ Reconnecting in 1 seconds. Press any key to exit local shell. . Connecting to 10.0.0.8:22... Connection established. To escape to local shell, press 'Ctrl+Alt+]'. WARNING! The remote SSH server rejected X11 forwarding request. Last login: Wed Apr 1 13:51:28 2020 from 10.0.0.1 [root@centos8 ~]#echo $PI [root@centos8 ~]#
位置变量
位置变量:在bash shell中内置的变量, 在脚本代码中调用通过命令行传递给脚本的参数
$1, $2, ... 对应第1个、第2个等参数,shift [n]换位置 $0 命令本身,包括路径 $* 传递给脚本的所有参数,全部参数合为一个字符串 $@ 传递给脚本的所有参数,每个参数为独立字符串 $# 传递给脚本的参数的个数 注意:$@ $* 只在被双引号包起来的时候才会有差异
清空所有位置变量
set --
范例:
[root@centos8 ~]#cat /data/scripts/arg.sh
#!/bin/bash
#
#********************************************************************
#Author: wangxiaochun
#QQ: 29308620
#Date: 2020-04-01
#FileName: arg.sh
#URL: http://www.magedu.com
#Description: The test script
#Copyright (C): 2020 All rights reserved
#********************************************************************
echo "1st arg is $1"
echo "2st arg is $2"
echo "3st arg is $3"
echo "10st arg is ${10}"
echo "11st arg is ${11}"
echo "The number of arg is $#"
echo "All args are $*"
echo "All args are $@"
echo "The scriptname is basename $0"
[root@centos8 ~]#bash /data/scripts/arg.sh {a..z}
1st arg is a
2st arg is b
3st arg is c
10st arg is j
11st arg is k
The number of arg is 26
All args are a b c d e f g h i j k l m n o p q r s t u v w x y z
All args are a b c d e f g h i j k l m n o p q r s t u v w x y z
The scriptname is arg.sh
范例:删库跑路之命令rm的安全实现
[root@centos8 ~]#cat /data/scripts/rm.sh
#!/bin/bash
#
#********************************************************************
#Author: wangxiaochun
#QQ: 29308620
#Date: 2020-04-01
#FileName: /data/scripts/rm.sh
#URL: http://www.magedu.com
#Description: The test script
#Copyright (C): 2020 All rights reserved
#********************************************************************
WARNING_COLOR="echo -e \E[1;31m"
END="\E[0m"
DIR=/tmp/date +%F_%H-%M-%S
mkdir $DIR
mv $* $DIR
${WARNING_COLOR}Move $* to $DIR $END
[root@centos8 ~]#chmod a+x /data/scripts/rm.sh
[root@centos8 ~]#alias rm='/data/scripts/rm.sh'
[root@centos8 ~]#touch {1..10}.txt
[root@centos8 ~]#rm *.txt
Move 10.txt 1.txt 2.txt 3.txt 4.txt 5.txt 6.txt 7.txt 8.txt 9.txt to /tmp/2020-04-01_15-15-28
范例:$*和$@的区别
[root@centos8 scripts]#cat f1.sh #!/bin/bash echo "f1.sh:all args are $@" echo "f1.sh:all args are $*" ./file.sh "$*" [root@centos8 scripts]#cat f2.sh #!/bin/bash echo "f2.sh:all args are $@" echo "f2.sh:all args are $*" ./file.sh "$@" [root@centos8 scripts]#cat file.sh #!/bin/bash echo "file.sh:1st arg is $1" [root@centos8 scripts]#./f1.sh a b c f1.sh:all args are a b c f1.sh:all args are a b c file.sh:1st arg is a b c [root@centos8 scripts]#./f2.sh a b c f2.sh:all args are a b c f2.sh:all args are a b c file.sh:1st arg is a
退出状态码变量
当我们浏览网页时,有时会看到下图所显示的数字,表示网页的错误信息,我们称为状态码,在shell脚本中也有相似的技术表示程序执行的相应状态。
进程执行后,将使用变量 $? 保存状态码的相关数字,不同的值反应成功或失败,$?取值范例 0-255
$?的值为0 #代表成功 $?的值是1到255 #代表失败
范例:
ping -c1 -W1 hostdown &> /dev/null echo $?
范例:
[root@centos8 scripts]#curl http://www.wangxiaochun.com &> /dev/null [root@centos8 scripts]#echo $? 0
用户可以在脚本中使用以下命令自定义退出状态码
exit [n]
注意:
- 脚本中一旦遇到exit命令,脚本会立即终止;终止退出状态取决于exit命令后面的数字
- 如果未给脚本指定退出状态码,整个脚本的退出状态码取决于脚本中执行的最后一条命令的状态码
展开命令行
展开命令执行顺序
把命令行分成单个命令词
展开别名
展开大括号的声明{}
展开波浪符声明 ~
命令替换$() 和 ``
再次把命令行分成命令词
展开文件通配*、?、[abc]等等
准备I/0重导向 <、>
运行命令
防止扩展
反斜线(\)会使随后的字符按原意解释
范例:
echo Your cost: \$5.00 Your cost: $5.00
加引号来防止扩展
单引号(’’)防止所有扩展 双引号(”“)也可防止扩展,但是以下情况例外:$(美元符号)
变量扩展
`` : 反引号,命令替换 \:反斜线,禁止单个字符扩展 !:叹号,历史命令替换
脚本安全和 set
set 命令:可以用来定制 shell 环境
$- 变量 h:hashall,打开选项后,Shell 会将命令所在的路径hash下来,避免每次都要查询。通过set +h将h选项关闭 i:interactive-comments,包含这个选项说明当前的 shell 是一个交互式的 shell。所谓的交互式shell,在脚本中,i选项是关闭的 m:monitor,打开监控模式,就可以通过Job control来控制进程的停止、继续,后台或者前台执行等 B:braceexpand,大括号扩展 H:history,H选项打开,可以展开历史列表中的命令,可以通过!感叹号来完成,例如“!!”返回上最近的一个历史命令,“!n”返回第 n 个历史命令
范例:
[root@centos8 ~]#echo $-
himBHs
[root@centos8 ~]#set +h
[root@centos8 ~]#echo $-
imBHs
[root@centos8 ~]#hash
-bash: hash: hashing disabled
[root@centos8 ~]#echo {1..10}
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10
[root@centos8 ~]#echo $-
imBHs
[root@centos8 ~]#set +B
[root@centos8 ~]#echo $-
imHs
[root@centos8 ~]#echo {1..10}
{1..10}
set 命令实现脚本安全
-u 在扩展一个没有设置的变量时,显示错误信息, 等同set -o nounset -e 如果一个命令返回一个非0退出状态值(失败)就退出, 等同set -o errexit -o option 显示,打开或者关闭选项 显示选项:set -o 打开选项:set -o 选项 关闭选项:set +o 选项 -x 当执行命令时,打印命令及其参数,类似 bash -x
范例:
[root@centos8 ~]#set -o
allexport off
braceexpand on
emacs on
errexit off
errtrace off
functrace off
hashall on
histexpand on
history on
ignoreeof off
interactive-comments on
keyword off
monitor on
noclobber off
noexec off
noglob off
nolog off
notify off
nounset off
onecmd off
physical off
pipefail off
posix off
privileged off
verbose off
vi off
xtrace off
本文链接:https://www.yunweipai.com/34323.html





网友评论comments